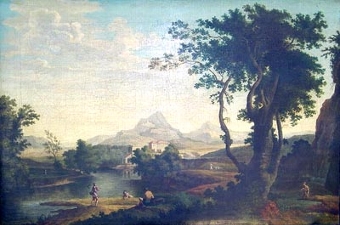the basilica di san giovanni e paolo, venice
- View other items in:
- antiques interior design modern and vintage
- other interior design
artware ltd
Enquire about this antique
Artware Ltd has 565 antiques for sale.
click here to see them all
The Basilica di San Giovanni e Paolo, known in the Venetian dialect as San Zanipolo, is a church in Venice, northern Italy. One of the largest churches in the city, it has the status of a minor basilica. After the 15th century the funeral services of all of Venice''s doges were held here, and twenty-five doges are buried in the church. A huge brick edifice built in the Italian Gothic style, it is the principal Dominican church of Venice, and as such was built for preaching to large congregations. It is dedicated to John and Paul, not the Biblical Apostles of the same names, but two obscure martyrs of the Early Christian church in Rome, whose names were recorded in the 3rd century but whose legend is of a later date.
In 1246, Doge Jacopo Tiepolo donated some swampland to the Dominicans after dreaming of a flock of white doves flying over it. The first church was demolished in 1333, when the current church was begun. It was not completed until 1430.The vast interior contains many funerary monuments and paintings, as well as the Madonna della Pace, a miraculous Byzantine statue situated in its own chapel in the south aisle, and a foot of St Catherine of Siena, the church''s chief relic.San Giovanni e Paolo is a parish church of the Vicariate of San Marco-Castello. Other churches of the parish are San Lazzaro dei Mendicanti, the Ospedaletto and the Beata Vergine Addolorata.
Bartolomeo Bon (the great west doorway)
Cima da Conegliano or Giovanni Martini da Udine (Coronation of the Virgin in the south transept)
Piero di Niccol? Lamberti and Giovanni di Martino (tomb of Doge Tommaso Mocenigo in the north aisle)
Gregorio Lazzarini (sala S. Tommaso)
Pietro Lombardo (tombs of Doge Pietro Mocenigo on the west wall and Doges Pasquale Malipiero and Nicolo Marcello in the north aisle; tomb of Alvise Diedo in the south aisle)
Tullio Lombardo ( and Alessandro Leopardo?) (tomb of Doge Andrea Vendramin on the north wall of the choir)
Lorenzo Lotto (St Antonine in the south transept)
Rocco Marconi (Christ between SS Peter and Andrew in the south transept)
Giovanni Battista Piazzetta (St Dominic in Glory on the ceiling of the Capella di San Domenico)
Veronese (The Assumption, The Annunciation and The Adoration of the Magi on the ceiling of the Capella del Rosario; The Adoration of the Shepherds in the Capella del Rosario). The famous The Feast in the House of Levi, painted for the refectory, is now in the Accademia Gallery.
Alessandro Vittoria (St Jerome in the north aisle)
Alvise Vivarini (Christ carrying the Cross in the sacristy)
Bartolomeo Vivarini (Three Saints in the north aisle)
Venice is a city in northern Italy known both for tourism and for industry, and is the capital of the region Veneto, with a population of the whole Comune of about 270,660 (census estimate 30 April 2009). Together with Padua and Treviso, the city is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE) (population 1,600,000).
Antiques.co.uk Ref: HC96CAAY
- Materials:
- Pencil and Watercolour
- Width (cm):
- 11 x 15 in. 28 x 38 cm.
Artware Ltd
Artware Fine Art specialises in fine antique, decorative and historical portraits and topographical pictures . We cover a period from the 17th and 18th centuries through to the 19th & 20th Centuries. We have over 150 portraits in stock, which can be viewed on our web site, each historical portrait has well researched biographical information both on the sitter and the artist.
Contact details
18 La gare
51 Surrey row
London
Greater London
SE1 0BZ
UNITED KINGDOM
T: 0207 921 97904
E: greg@artwarefineart.com
W: www.artwarefineart.com